Call Center Quality Assurance (QA) main purpose is to ensure your contact center delivers great customer service. Learn about how mySQM™ Auto QA, the #1 Ranked Software on G2 for Customer Satisfaction for the Americas Market, can help you deliver great customer service on every call.
#1 Ranked QA Tool on G2 for User CSat for the Americas Market
mySQM™ Auto QA Demo Video Request
Is Call Center Quality Assurance Broken?
Did you know that 83% of agents do not feel their quality assurance program helps them improve customer satisfaction, and 7 out of 10 companies believe their QA program is broken for monitoring and improving call quality service?
The level of support and customer experience delivery your contact center delivers to customers is essential to the company's ability to achieve or maintain a positive reputation and good customer relationship.
Most call center managers believe that their QA program is broken to help them improve or consistently achieve great customer satisfaction, so it is appropriate to consider the following questions.
Is your QA program broken to help improve your customer satisfaction? Can you benchmark your QA metrics and KPIs within your company or against other companies to see how you are performing? How do you ensure that your agents meet customer service behavior standards? Furthermore, if agents do not meet the behavior standards, what will you do about it?
So, let's get started by looking at what call center QA is, why it matters, and the top 10 call center quality assurance best practices.
What is Call Center Quality Assurance?
Call center quality assurance is the process of monitoring and evaluating customer interactions to ensure that the service provided meets predefined standards and enhances customer satisfaction. The goal of QA in a call center is to maintain high levels of service quality, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that agents adhere to company policies, scripts, and regulatory requirements.
Furthermore, quality assurance assessment ensures call compliance adherence to specific guidelines, regulations, and standards during customer interactions, typically over the phone or chat, in a contact center environment. It ensures that agents follow both legal requirements (such as data protection laws like GDPR or HIPAA) and internal company policies (such as approved scripts, conduct codes, and quality standards).
QA and Total Quality Management (TQM) in a call center environment differ in their scope, focus, and methodologies, even though both aim to improve service quality. TQM is a holistic approach that seeks to improve every aspect of the call center's operations to enhance overall quality. TQM encompasses continuous improvement in all areas, including the voice of the customer (VoC) closed-loop (IDCA) improvement process, service delivery, employee satisfaction, operational efficiency, and organizational culture.
Listed below are the basic elements of a call center QA program.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly listen to or review recorded customer experience (CX) interactions to assess agent performance.
- QA Scorecards: Using standardized evaluation forms to score interactions based on specific agent behavior standards and metrics, such as understanding, helping, caring, resolution, compliance, and call handling time.
- Training and Coaching: Providing constructive feedback to agents based on the evaluations, identifying areas for improvement, and offering training or coaching sessions.
- Performance Metrics: Tracking and benchmarking key performance indicators (KPIs) like customer satisfaction, first-call resolution, average handle time, and call compliance adherence displayed on QA scorecards and dashboards.
- Continuous Improvement: Using VoC closed-loop insights from QA data to refine training programs, update scripts, improve processes, and enhance customer experience.
Benefits of Call Center Quality Assurance:
A well-crafted and effectively executed call center quality assurance program can have a profound impact on a business. Here's why QA matters:
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Ensures that customers consistently receive high-quality service to help build a strong service reputation and customer retention. In the last year, 40% of the population made at least one choice to switch to a different company because of poor customer experience.
- Increased First Call Resolution: FCR is the leading indication for achieving great customer satisfaction; in fact, 9 out of 10 times, when a customer is not satisfied, the reason is they did not experience an FCR interaction. With every 1% improvement in first-call resolution, there is a 1% improvement in customer satisfaction rates.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Data shows that call center QA can significantly enhance compliance and risk management. Moreover, effective QA compliance and risk management practices are 30% less likely to face regulatory actions due to non-compliance compared to those with weak or non-existent QA practices.
- Increased Efficiency: Call centers with effective QA practices achieve a 5-15% higher FCR rate, resulting in fewer callbacks and operational savings of $286,000 for every 1% improvement in FCR. Furthermore, call centers implementing regular QA reviews can see a reduction in average handle time of 15-20%, resulting in significantly improving agent productivity and lower costs.
-
Return on Investment: mySQM™ automated QA tool can lead to an ROI of up to 600% and improve customer satisfaction scores, reducing repeat calls by up to 40%. mySQM™ auto QA solution uses AI to evaluate 100% of the calls. mySQM™ tool features include manual, automated, or a blend of the two QA evaluation methods.
Top 10 Call Center Quality Assurance Best Practices
With a robust quality assurance process in place, your call center can consistently maintain operational efficiency, deliver fast and effective customer service, and ensure agents perform at their highest level. Let's explore some of the best practices for call center QA that can help you achieve these goals.

![]()
QA Metrics and KPIs are perhaps the most crucial step in your call center quality assurance program to identify the specific metrics and KPIs you want to measure and benchmark. It is vital to select metrics and KPIs that are both measurable and aligned with your call center's objectives, such as Customer Satisfaction, First Call Resolution, CX Sentiment, Total QA Score, Compliance, and Average Handle Time (AHT).
Given the numerous metrics and KPIs available, it is important to track those that best reflect your call center's goals and objectives. For example, suppose your priority is delivering efficient, high-quality customer service with effective resolution. In that case, you should focus on KPIs like Customer Satisfaction, CX Sentiment, Average Handle Time, and First Call Resolution.
![]()
Customer experience agent behavior standards are a set of guidelines and expectations designed to ensure that agents consistently deliver a positive and effective experience for customers during every interaction. These standards define the specific behaviors, communication styles, and service practices that agents should follow to meet or exceed customer expectations and align with the company's customer service goals.
Key components of these behavior standards typically include Friendliness and Courtesy, Active Listening, Empathy and Emotional Intelligence, Clear and Effective Communication, Problem-Solving and Resolution Skills, Positive Attitude, and Adherence to Procedures and Compliance.
These standards are designed to create a consistent, high-quality customer experience across all interactions, helping to build customer satisfaction, loyalty, and trust. Organizations measure adherence to these standards through quality assurance programs, customer feedback, and performance metrics, using the results to guide coaching, training, and development efforts.
![]()
Manual call center QA involves human evaluators, often quality assurance evaluators or supervisors, who listen to recorded calls or monitor live interactions to assess agent performance against predefined criteria. This approach allows for nuanced judgment and qualitative feedback, such as evaluating tone, empathy, and adherence to soft skills. However, it can be time-consuming, subject to human error or bias, and limited in scope due to the time and effort required to review each interaction individually.
Automated call center QA uses software and artificial intelligence (AI) to automatically analyze and evaluate up to 100% of customer interactions. This approach can process large volumes of data quickly, identify trends, and provide real-time insights by measuring performance against metrics such as call duration, CX sentiment analysis, compliance, and the ability to predict customer satisfaction. While automated QA is faster and more scalable, it may not fully capture the subtleties of human communication and might require fine-tuning to align with specific business objectives.
In summary, manual QA offers depth and a human touch in evaluating complex interactions, while automated QA provides speed, scalability, and data-driven insights. Many call centers use a combination of human and auto QA methods to achieve the positive aspects of each approach for their quality assurance program.

![]()
Using AI for call center QA to determine service quality delivery involves implementing technologies that analyze, evaluate, and improve customer interactions systematically. Here's a structured approach to leveraging AI in this context:
Automated Call Analysis
- Speech Recognition: AI-driven speech recognition converts spoken words into text, allowing for detailed analysis of conversations. This helps assess the content of interactions and identify whether agents follow scripts or guidelines.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP algorithms analyze the text for sentiment, intent, and contextual understanding. This enables the evaluation of how well agents address customer needs and maintain a positive tone.
Performance Scoring
- Automated Scoring Systems: AI can automatically score calls based on predefined criteria, such as adherence to CX behavior standards, resolution effectiveness, compliance with company policies, and predicted CSat, which can be displayed on the agent QA scorecard and dashboard.
- Customizable Metrics: AI systems can be configured to evaluate specific KPIs relevant to service quality, such as FCR, CSat, AHT, Compliance, and CX Sentiment.
Customer Sentiment Analysis
- Sentiment Analysis: AI tools assess the sentiment expressed by customers during interactions, identifying positive, neutral, or negative sentiments. This helps gauge the overall customer experience and predict customer satisfaction.
- Feedback Integration: AI can analyze customer feedback from various sources (QA data, surveys, social media, etc.) to provide a comprehensive view of service quality.
Trend and Pattern Detection
- Trend Analysis: AI can identify trends and patterns in service quality data over time, such as recurring issues or common areas of improvement. This helps in understanding systemic problems and addressing them proactively.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can predict customer satisfaction that can be used to track and benchmark service quality delivery
Compliance and Adherence Checks
- Automated Compliance Monitoring: AI systems can track adherence to regulatory requirements and internal policies during interactions, ensuring that agents follow necessary protocols and guidelines.
- Error Detection: AI can detect and flag errors or deviations from standard procedures, providing detailed reports for review and corrective action.
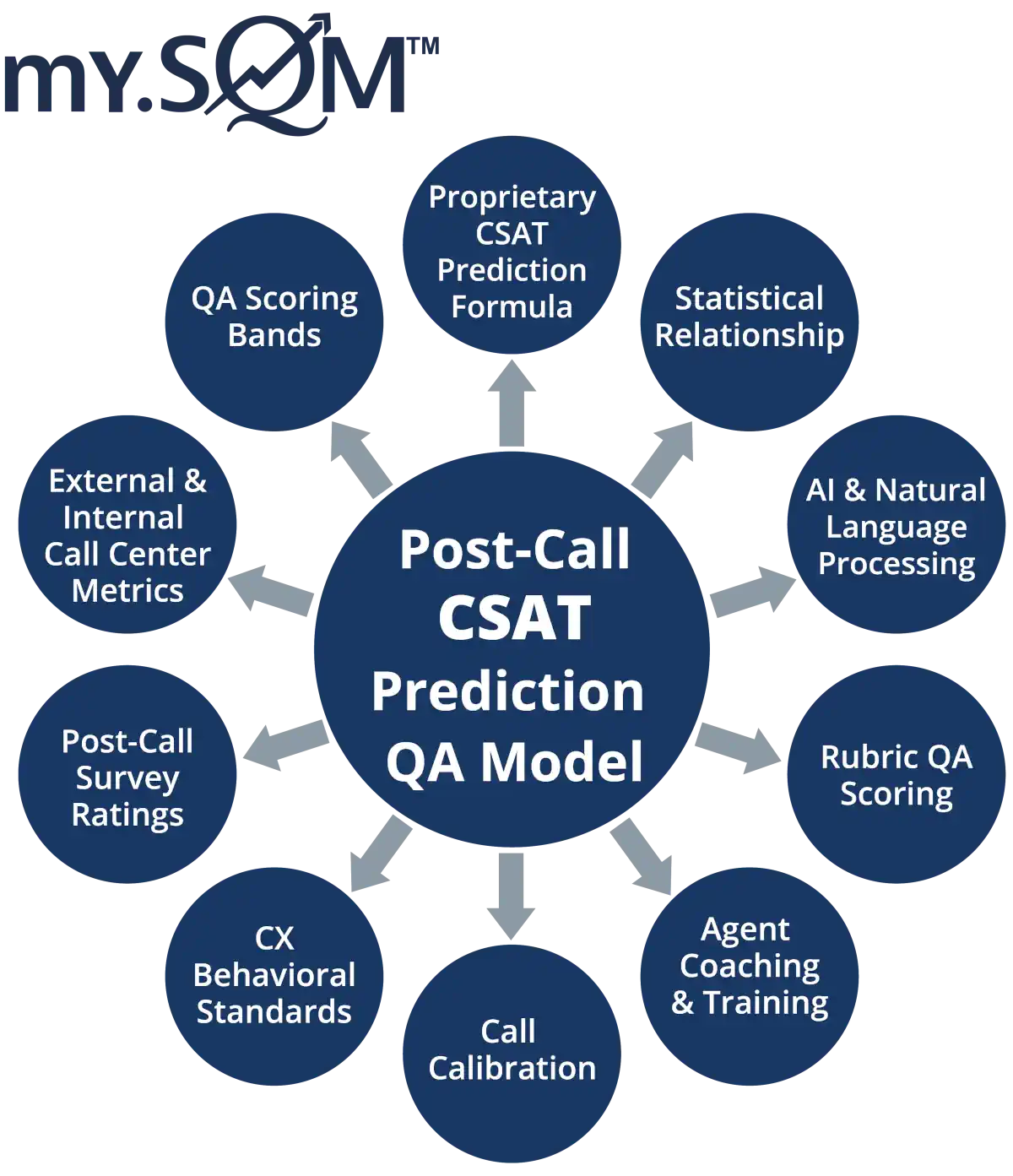
Predicting Customer Satisfaction - A Game Changer
Our Post-Call CSat Prediction QA Model uses AI, machine learning, natural language processing, and regression analysis techniques to predict customer satisfaction after interacting with a call center.
Our proprietary Post-Call CSat Prediction QA Model leverages 10 key components to accurately predict agent QA CSat scores, achieving up to a 95% match with survey-based agent CSat ratings.
![]()
Agent Self-Coaching uses AI, which is a process where agents use AI-driven tools to guide their CSat performance improvement. AI analyzes customer interactions (e.g., calls, chats) for sentiment, tone, keywords, and adherence to scripts or behavior standards, providing instant feedback to agents on their performance.
Unlike traditional coaching, where supervisors or QA specialists provide feedback and training, self-coaching encourages agents to review their own calls or interactions independently, reflect on their performance, and identify areas for improvement based on AI insights.
Agent Self-Coaching typically involves providing agents with access to recorded calls, performance metrics, and quality assurance scores. Agents use this data to evaluate their interactions against key performance indicators (KPIs) such as Customer Satisfaction, First Call Resolution, and Average Handle Time. They can also identify strengths and weaknesses in areas like communication style, problem-solving skills, resolution, and adherence to company guidelines.
This approach helps agents build self-awareness, fosters a sense of ownership over their performance, and encourages continuous learning and development. It also reduces the burden on supervisors by allowing agents to address performance issues proactively before they become significant problems.
![]()
Agent Self-Training uses AI, which is a method where agents use AI-powered tools to assess and improve their CSat performance independently. AI provides insights, personalized feedback, and tailored learning resources, enabling agents to take control of their development and continuously enhance service quality.
Agent Self-Training for customer experience soft skills involves developing and enhancing the interpersonal soft skills needed to deliver exceptional customer service. These soft skills are crucial for creating positive interactions, building rapport, resolving issues effectively, and providing great customer satisfaction. Here are some key aspects of agent self-training for CX and FCR soft skills:
- Active Listening
- Caring and Empathy
- Communication
- Call Resolution
- Problem-Solving
Role-playing uses call reason simulation to resolve calls and deliver great customer satisfaction. Agents take quizzes and tests to gauge CX and FCR soft skills understanding and identify areas for improvement. Agent Self-Training is delivered through QA software.
![]()
Agent recognition and rewards program is a structured initiative designed to acknowledge and reward agents for achieving high performance in near real-time, meeting quality standards, and delivering great customer satisfaction. This program aims to motivate agents, boost morale, and encourage continuous improvement by celebrating their successes and contributions to the organization.
Agents are recognized and rewarded based on their QA scores, which measure their adherence to CX behavior standards and other key performance indicators such as CSat, FCR, CX Sentiment score, total QA score, and AHT. The following are examples of monetary and non-monetary rewards.
Monetary Rewards: Cash bonuses, gift cards, or commission-based incentives are provided to achieve high performance or meet specific targets.
Non-Monetary Rewards: Awards can include certificates, plaques, trophies, additional time off, or special privileges (like flexible schedules or preferred shifts).
Gamification techniques can be used where agents earn points, badges, or levels based on their performance, which can be redeemed for rewards or more cash bonuses.
A well-structured recognition and rewards program not only enhances agent motivation and engagement but also contributes to improved service quality, customer satisfaction, and overall organizational success.
![]()
QA calibration using post-call CX surveys involves aligning quality assurance evaluations with direct customer feedback collected immediately after a call or interaction. This process ensures that the internal assessment of an agent's performance aligns with the customer's perspective on service quality, satisfaction, and overall experience.
After a customer interaction, a post-call survey was conducted to gather immediate feedback on their experience. These surveys typically measure factors such as customer satisfaction and specific aspects of the service, like agent professionalism, empathy, and problem resolution.
The customer feedback from post-call surveys is compared with the internal QA evaluations of the same interaction. This comparison helps identify any discrepancies between how the QA team or AI assessed the interaction and how the customer perceived it.
Analyzing these gaps highlights differences in perspectives, such as instances where an agent received a high QA score or predicted CSat score, but the customer reported dissatisfaction, or vice versa.
During calibration sessions, the QA team reviews both the internal scores and customer feedback to align their evaluation criteria more closely with what customers value most. This helps ensure that QA metrics reflect actual customer priorities and satisfaction drivers. QA calibration based on the CX surveys process can be used in the manual and automated QA methods.
QA calibration using post-call CX surveys ensures that QA evaluations are aligned with the aspects of service that customers care most about, leading to improvements in customer satisfaction. In addition, it reduces subjectivity by incorporating objective customer feedback into the QA process, reducing the potential for bias or misalignment in internal evaluations.
![]()
QA root cause analysis is a systematic process used to identify the underlying reasons for recurring quality issues or performance gaps in call center operations. By understanding the root causes of these problems, call centers can implement targeted corrective actions to improve service quality, enhance customer satisfaction, and optimize agent performance.
Begin by pinpointing the specific issues or performance gaps revealed through QA evaluations. These could include high rates of customer dissatisfaction, low FCR, high AHT, frequent compliance violations, or any other recurring problems.
Collect data related to the identified problem from various sources, such as QA scores, customer feedback, post-call surveys, call recordings, agent performance metrics, and interaction logs.
Analyze the data to look for patterns, trends, or correlations that might indicate why the issue is occurring. For example, suppose low customer satisfaction scores are consistently associated with a specific type of call, agent behavior, or time of day. In that case, these patterns can provide clues to the underlying causes.
Based on the validated root causes, develop specific, actionable strategies to address the issues. These might include revising agent behavior standards, providing targeted agent training, adjusting processes, improving technology tools, or refining QA evaluation criteria. Implement these corrective actions systematically and monitor their effectiveness over time. To enhance your QA root cause analysis, it is helpful to use a voice of the customer closed-loop process where you identify, develop, check, and then act.
![]()
An Outside-in QA mindset in a call center context focuses on evaluating and improving quality assurance from the customer's perspective rather than solely relying on internal metrics, processes, or standards. The Outside-in QA approach emphasizes understanding and prioritizing the needs, expectations, and experiences of the customer to ensure that every aspect of the service aligns with delivering value and satisfaction to them.
The difference is that Outside-in CX operating practices are based on putting the customer first in terms of how they operate. Conversely, the Inside-out CX operating practices are based on putting the organization first. In many cases, when decisions are made with an Inside-out approach, they meet the company's needs but not the customers'.
Effective Outside-in QA processes are designed around what matters most to customers, such as empathy, resolution effectiveness, clear communication, and minimal effort. The focus is on measuring how well the call center meets these customer-centric criteria rather than internal performance metrics alone.
Direct feedback from customers, such as post-call surveys, CX Sentiment, Customer Satisfaction scores, and verbatim comments, is integrated into the QA process. This feedback helps identify gaps between customer expectations and the service delivered.
The QA process is continuously informed by evolving customer insights, preferences, and expectations. This may involve regularly updating QA scorecards, agent CX behavior standards criteria, and guidelines to reflect changing customer needs or customer satisfaction.
An Outside-in QA mindset shifts the focus from internal processes to customer experience, ensuring that all quality assurance efforts aim to achieve great customer satisfaction.
Does Your Call Center Use an Outside-In QA Approach to Deliver Great Csat?
4.6




 Stars on G2 for mySQM™ Auto QA Tool Reviews
Stars on G2 for mySQM™ Auto QA Tool Reviews












What Differentiates SQM from its Competitors is our...
mySQM™ Automated QA/CX Analytics Solution that uses proprietary AI technology and intellectual property to determine QA scores and predict customer satisfaction with up to 95% accuracy for every call. SQM's Post-Call Customer Satisfaction Prediction QA Model - Is a Game-Changer!
SQM's QA and CSAT scores can be used to benchmark against 500 enterprise level call centers. Analyze 100% of customer calls with our auto QA/CX solution.
Furthermore, mySQM™ QA/CX provides agents with self-coaching, self-training, and real-time financial recognition features for calls evaluated to help monitor, motivate, and manage agents to deliver great customer satisfaction.
mySQM™ Auto QA ROI Calculator
Discover Your Savings in Minutes