What is Customer Journey Mapping?
The essence of customer experience journey mapping is to walk in the customer's shoes as they interact with an organization using different touchpoints. As such, CX journey mapping focuses on the entire end-to-end journey for using an organization's products and/or services from the customer's perspective. Therefore, using CX journey mapping is an effective technique for improving customer experience using a touchpoint or multiple touchpoints to resolve the same inquiry or problem.
A VoC closed-loop process starts with identifying service gaps by capturing customer survey feedback and ends with actioning customer feedback. People, processes, policy, and technology improvements made to improve customer service must be verified by the customer that they improved their customer journey. The VoC closed-loop process can be applied to all touchpoints customer journey.

Expectations Using Different Contact Channels Touchpoints
An outstanding customer experience (CX) is now the competing differentiator for many organizations because it is very difficult to differentiate offerings based on products and pricing alone. Customers expect consistent service no matter what interaction or touchpoint they are experiencing, and they also expect their inquiry or problem to be resolved on the first contact.
SQM research shows that 93% of customers using the call center channel and 72% of customers using the website channel expect to resolve their inquiry or problem in one contact. However, customers' expectations to resolve any inquiry or problem on the first contact using any contact channel they choose is challenging for organizations to meet.
Furthermore, SQM's research shows a whopping 42% of customers do not experience One Contact Resolution (OCR) when using a contact channel touchpoint to resolve an inquiry or problem. The OCR metric is defined as a customer's inquiry or a problem resolved in one contact using only one contact channel. For customers who experienced non-OCR, it results in a 15% decrease in customer satisfaction (top box survey response rating) when two contacts or channels are used to trying to resolve their inquiry or problem.
Listening Posts for Customer Experience Journey Mapping
Providing world-class CX and creating a consistent experience for customers across all the major interactions and touchpoints is a challenge and a goal for many organizations. Therefore, improving CX is a top priority for most leading North American organizations. 46% of SQM clients have used some form of journey mapping to understand and improve customer experience using a contact channel touchpoint.
However, only a small percentage of organizations felt that CX improved due to their CX journey mapping efforts. Based on the fact that customers use multiple contact channels, either independently or simultaneously, it is essential that organizations do a better job at understanding their customers' entire experiences when interacting with the organization's touchpoints.
Furthermore, organizations need to understand the customer journey of using multiple channels to resolve the same inquiry or issue, especially when you consider that over 40% of customers interacting with an organization use multiple contact channels to resolve the same inquiry or problem. We recommend our top 10 CX metrics for understanding and measuring the customer journey doing business with your organization.
The Top 10 customer experience metrics apply to any industry and customer contact channels to resolve an inquiry or problem. The Top 10 CX Metrics are based on SQM's experience of measuring, tracking, and benchmarking over 500 leading North American organizations and surveying over 5 million customers who used a contact channel. SQM has been conducting Voice of the Customer (VoC) contact channel CX benchmarking studies since 1996.

To provide outstanding experiences for customers, more progressive and customer-centric organizations are now taking an integrated approach for understanding CX. These organizations use overlapping CX listening posts to capture the (VoC) data to understand the entire CX truly.
In addition, they are using this data to dive deeper with CX journey mapping rather than just using big data analytics to understand what their customers are experiencing when conducting business. Put simply, they have a comprehensive understanding of the customer's end-to-end experience that is based on conducting VoC survey research and in-depth interviews.
Figure 1 shows the three overlapping listening posts that are most useful for capturing VoC for a comprehensive understanding of CX to create an in-depth CX journey map:
- Touchpoint Transactional Surveys
- Interaction Relationship Surveys, and
- CX Journey Mapping In-depth Interviews
Figure 1: CX Listening Posts

The CX listening posts are comprised of in-depth customer interviews, measuring customer relationships, and transactional surveys. Transactional-based surveys are conducted to understand touchpoint-specific CX. Conversely, relationship-based surveys are undertaken to understand interaction lifecycle stage-specific CX.
The CX journey mapping interview is an in-depth interview with customers who do business with your organization and focuses on the interactions and touchpoints your customers have experienced. These interviews can occur individually or in a small focus group setting.
One of the biggest challenges of CX journey mapping is finding customers to do an in-depth interview with who can provide quality experience feedback for all lifecycle stages and touchpoints.
It is considered best to conduct interaction relationship surveys and touchpoint transactional surveys before conducting CX journey mapping in-depth interviews to ensure the discussions dive deeper into the pain points or lifecycle stages that are most important to the customer.
By conducting VoC transactional and relationship survey research before conducting CX journey mapping in-depth interviews, interviewers have more CX background knowledge for conducting an effective in-depth interview. In addition, the use of relationship and transactional survey listening posts (e.g., large sample size) and in-depth interviews (e.g., detailed feedback) provides comprehensive and integrated insights for understanding CX.
The sample size for touchpoint transactional surveys should be at least 400 customer surveys per contact channel. In addition, the contact channels to survey should be with your primary touchpoints (i.e., Web self-service, call center, chat, email, and self-service IVR).
Transactional surveys should be conducted within one business day of using a touchpoint. The shortfall with interaction relationship and touchpoint transactional surveys is that they are not as in-depth for providing detailed CX feedback compared to journey mapping in-depth interviews. However, relationship and transactional surveys give a statistically accurate CX measurement.
The interaction relationship survey should have a sample size of at least 400 customers. The survey should focus on the interaction lifecycle stages (e.g., brand awareness, purchasing, onboarding, servicing, and renewing). Having a large customer survey sample size will assist in accurately understanding customer needs and CX ratings for the interaction lifecycle stages of each persona.

For CX journey mapping in-depth interviews, we recommend a minimum sample size of 10 customers per persona (e.g., school teacher, retired person, student). It is common practice for an organization to conduct over 50 in-depth interviews on an annual basis.
An effective interviewer should be able to conduct three to five in-depth interviews daily. For CX journey mapping in-depth interviewing, it is also important that an interviewer knows how to conduct effective interviews and focus groups for CX journey mapping. In addition, the interviewer needs to be able to ask the right types of questions, be a great listener, and accurately capture CX feedback.
It is critical for the interviewer to ask the customer to describe their needs and provide CX ratings for each interaction. Understanding the customer's needs and their CX ratings are both critical components to the journey mapping process. In this step, the interviewer finds out about CX by asking high-level questions that focus on interactions, not CX using touchpoints.
The interviewer should ask the following high-level questions:
- Did your interaction (e.g., brand awareness, purchasing, onboarding, servicing, renewing) experience meet your expectations? Why?
- Do you have any CX improvement suggestions?
- Based on your interaction, overall, how satisfied are you with your experience using a touchpoint? Why?
Note: The above three questions should be asked for each interaction stage.
- Thinking about your entire experience as a customer of XYZ Company, how would you rate your overall customer experience?
- On a scale of 0 to 10, where 0 means not at all likely and 10 means extremely likely, how likely are you to continue to do business with XYZ Company?
- On a scale of 0 to 10, where 0 means not at all likely and 10 means extremely likely, how likely are you to recommend XYZ Company to a friend or colleague?
Note: The above three questions should be asked based on the entire CX.
Download contact channel top 10 CX metrics survey questions by clicking the below image link.
Organizations should determine CX improvement opportunities based on VoC survey research and compare them with improvement suggestions from the CX journey mapping in-depth interview to make a case for change.
Once the CX journey mapping efforts are completed, they need to be shared with key stakeholders. By using the three overlapping listening posts for capturing the voice of the customer, an organization not only gains a comprehensive understanding of CX but will also have a body of evidence about the best opportunities to improve the customer journey experience.
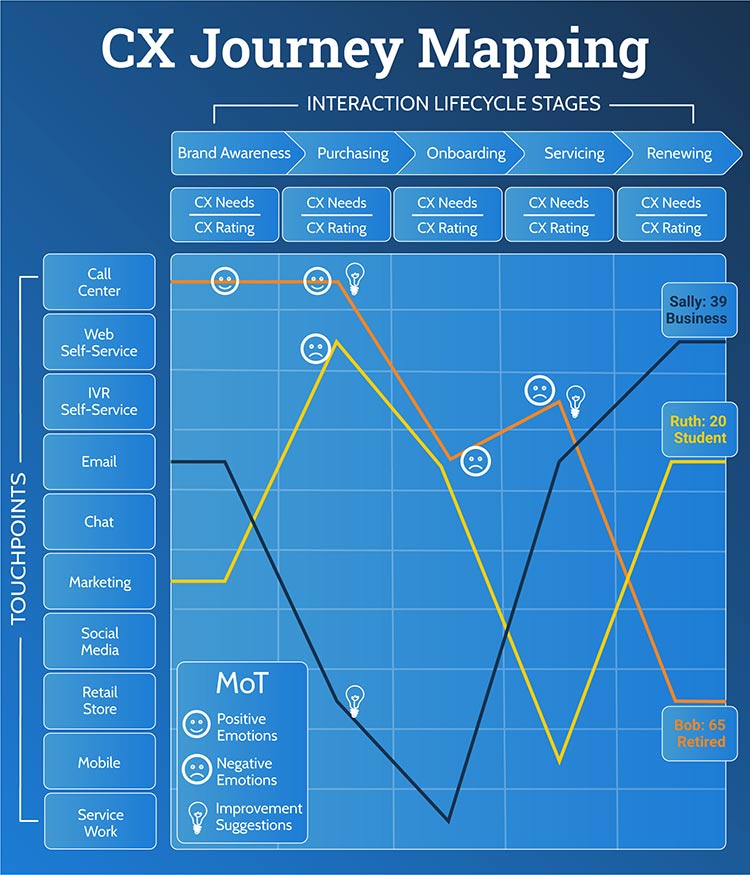
Customer Experience Journey Map Template
The below figure shows a common CX journey mapping template being used. The CX journey map is created based on a skilled interviewer asking a customer about their interaction lifecycle stages and touchpoint Moments of Truth (MoT) experiences when using the organization's products and/or services.
The horizontal axis shows an example of customer interactions with an organization based on their lifecycle stage (e.g., brand awareness, purchasing, onboarding, servicing, renewing). By evaluating lifecycle stages, you gain an understanding of the entire end-to-end CX.
For each interaction stage, the organization must understand the CX needs and the CX ratings. For each interaction, a customer uses a touchpoint. The vertical axis shows examples of touchpoints (e.g., call center, website, face-to-face). For each touchpoint used in the CX journey, the customer provides MoT experience feedback, emotion experience, and improvement suggestions.
Based on customer interviews, the interaction and touchpoint CX are plotted on the journey map. All essential MoT experience feedback is captured. In addition, moT experiences that drive positive emotions, negative emotions, and improvement suggestions are identified.
10 Essential Steps for Customer Experience Journey Mapping
There are many ways to create a CX journey map. However, the following is a high-level summary of the 10 essential steps we use for creating a CX journey map:
- Identify customer interactions (e.g., brand awareness through to renewing) lifecycle stages that a customer could potentially experience
- Identify touchpoints (e.g., marketing, social media, call center, IVR, email, face-to-face) that a customer could potentially experience
- Identify MoT (e.g., greeting a customer, resolving an issue) for each touchpoint that a customer could potentially experience
- Identify personas (e.g., retiree, business person, student) for whom you want insights about their CX interactions with an organization's touchpoints
- Understand customer needs and determine CX VoC ratings for each interaction and touchpoint, and mark your known pain points. This step is based on customer in-depth interviews and customer survey research
- Plot customer interaction and touchpoint experiences for each customer
- Determine interaction and touchpoint MoT and document the critical MoT that each customer experienced. This step is based on customer face-to-face interviews
- Determine customer's emotional experience and document for each interaction and touchpoint MoT. This step is based on customer face-to-face interviews
- Determine customer improvement suggestions and document for each interaction and touchpoint MoT. This step is based on customer face-to-face interviews
- Use CX journey mapping insights as to the foundation for developing an action plan for improving CX
Advantages and Disadvantages of CX Journey Mapping

5 Powerful Advantages
1. Holistic view of CX – the main advantage of CX journey mapping is its focus on the customer's entire journey (e.g., brand awareness through to renewing) when using an organization's products and/or services. Focusing on the entire customer journey versus only the individual touchpoint or interaction provides a holistic view of CX that can be very helpful in understanding and improving the customer's experience.

2. Understand CX better – the essence of the CX journey mapping process is that it allows you to walk in the customer's shoes as they interact with your organization through their lifecycle stages. Put simply, CX journey mapping is an outside-in approach. Having a trained interviewer conduct in-depth interviews with customers who interact with an organization's touchpoints provides a better understanding of the CX. The in-depth interview gives the organization valuable and detailed insights into customer interactions and touchpoint MoT experiences. VoC relationship and transactionla survey research and in-depth interviews are all used to understand CX better.

3. Discover CX improvement opportunities – an effective CX journey map provides insights on customer expectations at every significant interaction using a touchpoint, how well the organization is doing at meeting those expectations, customer emotion experience, and, most importantly, what the opportunities are for improving CX. Again, the CX journey mapping process is an outside-in approach. The outside-in approach allows the organization to use CX feedback and apply it to its people, processes, and technology practices.

4. Visual CX journey map – an infographic portrayal of CX is helpful for conveying current and future CX to all stakeholders. CX journey maps can be presented using journey mapping software, PowerPoint presentations, a condensed one-page handout, or any other appropriate manner for your organization. It is important to remember that when the stakeholders easily understand the CX journey map, they are typically more willing to develop and implement solutions for improving CX.

5. Foundation for developing an action plan – the CX journey map insights are the foundation for developing an action plan. In other words, the information garnered from the CX journey map is not an action plan in and of itself. Instead, the action plan needs to be based on the CX journey map insights that show the interaction and touchpoint MoT, which have CX dissatisfaction and/or negative CX emotions. Based on identifying the CX dissatisfaction and/or negative CX emotions, an organization can develop an action plan to implement solutions for eliminating or reducing the touchpoint MoT driving those experiences.

3 Potential Pitfall Disadvantages
- CX focused on intangibles – if the improvement efforts are focused too much on intangibles (e.g., Agent soft skills) versus tangibles (e.g., reducing repeat contact reasons for resolving the same inquiry or problem), then there is a good chance that overall CX will not improve. CX journey mapping has a bad reputation for focusing on areas that do not positively impact CX.
- Limited CX feedback – most customers cannot remember every interaction and touchpoint they used with an organization. Each customer is different, so if the journey mapping process only sources feedback from a small number of customers, then this might not provide a representative sample of what most of your customers have experienced. If Csat survey research for interactions and touchpoints is not used to supplement CX journey mapping interviews, then the wrong areas may be selected for improvement, or CX may not improve.
- Not actionable – if the CX journey map is oversimplified, it can be difficult to identify improvement opportunities. Conversely, if the CX journey map has too much information, it can also be difficult to explain and identify improvement opportunities. The CX journey map must help identify and explain improvement opportunities. One of the primary purposes is to use the CX journey map as the foundation for developing an action plan. It is necessary to focus on the CX improvement feedback and the visual CX journey map. CX improvement opportunities require working collaboratively with other departments (e.g., IT, finance, marketing, HR, service), which can be very difficult because of the siloed nature of many departments.


