Delivering an exceptional customer experience (CX) isn't just a goal—it's a necessity. To achieve this, leveraging call center CX analytics reporting is essential. By understanding and implementing best practices in reporting, businesses can enhance their customer experience strategy effectively.
This blog will delve into actionable insights and tools that can optimize your approach, ensuring your call center not only meets but exceeds customer expectations.
Analytics are essential for managing customer experiences in call centers. They replace guesswork with solid data that can be turned into actionable insights. By examining interaction patterns, businesses can assess call handling times, pinpoint common customer issues, and gauge overall sentiment.
This detailed analysis supports better decision-making and enhances service quality. Additionally, effective analytics enable personalization by revealing individual customer journeys, helping agents address specific needs more accurately.

What are the Benefits of Effective CX Analytics Reporting?
CX analytics reporting provides numerous advantages that boost a call center's performance. First and foremost, it promotes data-driven strategies, helping identify both short-term and long-term trends pivotal for strategic planning. Here are some key benefits:
- Improved Csat: Analytics reveals the strengths and weaknesses of the current customer service strategy, providing insights to enhance customer interactions and resolve issues promptly.
- For example, a call center uses analytics to track customer feedback scores and call resolution times. The data reveals that customers are consistently dissatisfied with the time it takes to resolve their issues. By analyzing these metrics, the call center discovers that agents spend too much time navigating outdated knowledge bases. The center updates the knowledge base and implements faster access tools for agents. As a result, Csat scores improve because customers experience quicker resolutions and more effective interactions.
- Operational Efficiency: With clear metrics and performance indicators, management can streamline processes, allocate resources more effectively, and reduce operational costs.
- For example, analytics show that many calls are being transferred between departments. Further analysis reveals that many of these transfers are due to agents not having readily available information. The call center reduces unnecessary transfers by implementing a centralized information system and improving the call routing process based on the data. This streamlines operations, cuts down on average handling times, and lowers operational costs by improving overall efficiency.
- Proactive Problem Solving: Regular reporting identifies emerging issues before they escalate. This proactive approach allows for quicker resolutions, preventing potentially damaging situations.
- For example, the call center's analytics identify an increasing trend in call volumes related to billing issues over the past few weeks. Reporting highlights that a recent system update may have caused these problems. Before this issue affects a larger number of customers, the call center teams up with the IT department to fix the billing system. They also proactively communicate with customers about the resolution, preventing further frustration and potential damage to the center's reputation.
- Increased Agent Performance: Insights into performance metrics support the training and development of call center agents by highlighting areas for improvement.
- For example, analytics reveal that a subset of agents has lower first-call resolution rates compared to their peers. Detailed performance metrics show that these agents often struggle with handling complex queries. The call center uses this insight to develop targeted training programs focused on advanced problem-solving skills. After completing the training, the agents' performance improves, leading to better resolution rates and higher overall Csat.
What are the Best Practices for Data Collection and Management?
Accurate and insightful CX analytics hinge upon how well a call center manages and collects its data. It is imperative to establish a robust framework for data management to ensure that analytics can be effectively leveraged.

1. Ensuring Data Accuracy and Consistency
To derive meaningful insights, the data collected must be both accurate and consistent. This involves:
- Regular Audits: Conducting frequent audits of data collection processes to ensure the integrity and accuracy of data.
- Example: A call center notices discrepancies in call duration reports across different teams. To address this, they implement monthly audits to review data collection processes and correct any inconsistencies.
- Standardized Metrics: Ensuring consistency by standardizing metrics and definitions across all departments within the call center.
- Example: Establish a standard definition for metrics such as "first call resolution" and "average handling time" across all departments.
- Training Staff: Educating employees on the importance of data accuracy and involving them in maintaining standards.
- Example: A call center conducts workshops for its agents on the importance of accurate data recording provides guidelines on how to enter data correctly into the system.
Consistent data collection not only leads to more reliable reports but also builds the foundation for continuous improvement and strategic foresight.
2. Establishing Clear Data Collection Processes
A well-structured data collection process is the cornerstone of effective analytics reporting. Without clear procedures, data can become fragmented and unreliable. Here's how to fortify your data collection:
- Define Objectives: Before collecting data, clearly outline the objectives of what needs to be achieved. Understand what specific metrics are vital for your goals.
- Example: Before launching a new Csat survey, a call center outlines its objective: to measure the effectiveness of recent changes in call handling procedures. They identify key metrics like Csat scores and FCR rates that align with this objective, ensuring the collected data is relevant and actionable.
- Utilize Technology and AI: Automation and new AI tools can greatly speed up your reporting processes. They reduce the need for manual work, improve accuracy, and make the reporting faster. Plus, automated reports can significantly reduce human error and increase the reliability of collected data.
- Example: A call center integrates an AI-driven analytics platform that automatically collects and analyzes call data, such as wait times and customer feedback.
- Documentation and Guidelines: Establish comprehensive documentation and guidelines for data collection methods to ensure everyone follows the same protocol.
- Example: A call center creates a detailed manual outlining procedures for data entry, including step-by-step instructions and quality checks.
By implementing these processes, call centers can amass a wealth of information that's clear, accessible, and useful for analytics.
3. Handling Data Privacy and Security
As call centers collect vast amounts of personal information, maintaining data privacy and security is not just a best practice—it's a regulatory requirement. Protecting customer data builds trust and ensures compliance with data protection laws.
- Compliance: Stay updated with the latest regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, to ensure your practices align with legal standards.
- Data Encryption: Utilize data encryption both in transit and at rest to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Example: To protect customer data, the call center implements encryption protocols for all data transmitted between agents and the central database.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to limit who can view and handle data within the organization.
- Example: A call center sets up role-based access controls in its data management system. Only authorized personnel have access to sensitive customer information, while others have restricted access based on their job roles.
Handling data responsibly not only secures customer trust but also protects the call center from potential legal and financial repercussions. By prioritizing these practices, call centers can mitigate risks and focus on utilizing analytics for enhancing customer experience.
What are the Best Techniques for CX Reporting?
When striving for exceptional CX in call centers, effective reporting techniques are critical. These methods ensure that insights are not only gathered but also translated into actionable strategies that enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.

1. Utilizing Real-Time Dashboards and Reports
By providing up-to-the-minute insights, call center managers can identify issues as they arise, enabling immediate intervention before problems escalate.
- Instant Problem Resolution: Real-time data equips teams with the information needed to address customer complaints quickly, reducing wait times and improving service levels.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous access to performance metrics such as call volume, average handling time, and FCR rates allow for prompt adjustments to staffing and resources as needed.
For example, SQM's Agent Dashboard includes call resolution and Csat gauge chart widgets that provide performance score insights and action alerts widgets to identify service recovery and coaching opportunities. Also, the agent dashboard shows how they rank for Csat and call resolution; out of all the features of mySQM™ Customer Service QA Software, customers like the dashboard the best.
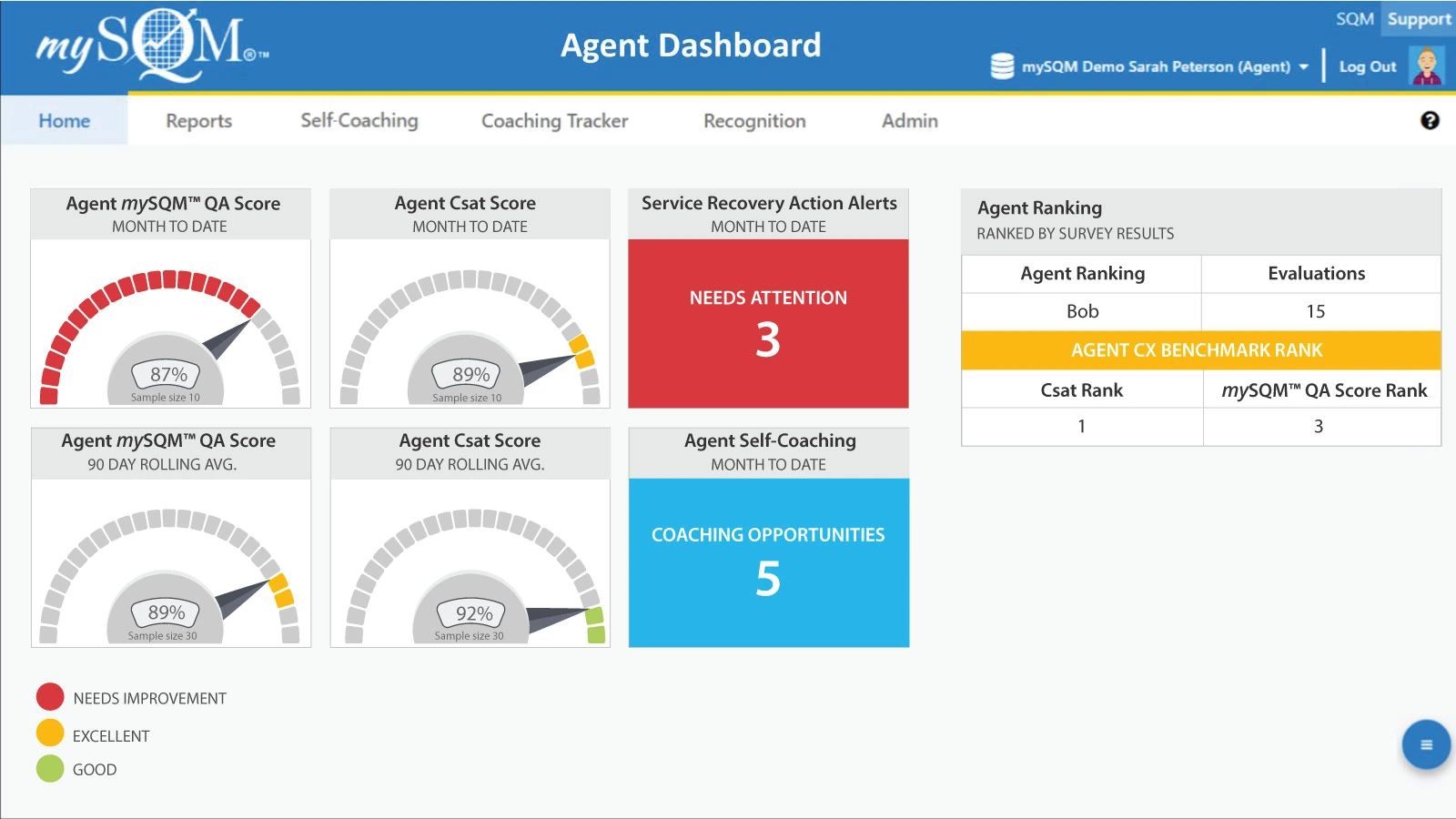
Real-time reporting tools should be integrated into the daily workflow to allow managers and team leaders to proactively manage operations and ensure a seamless customer experience.
2. Tailoring Reports for Different Stakeholders
A one-size-fits-all approach to reporting does not work when dealing with various stakeholders. Each group within an organization has unique needs and objectives, so it's crucial to tailor reports to address these differences effectively.
- Executives: Focus on high-level trends and strategic insights. Provide information that supports decision-making on resource allocation and long-term planning.
- Supervisors: Present detailed reports that highlight their team's performance, including individual metrics and comparative data to motivate and manage their staff effectively.
- Agents: Offer insights into their personal performance metrics, fostering a sense of ownership and self-improvement.
3. Data Visualizations for Better Insights
Visual data representation is one of the most powerful reporting techniques. Graphs, charts, and heat maps can transform complex datasets into accessible and actionable insights.
- Improved Comprehension: Visuals aid in understanding trends and patterns without wading through cumbersome spreadsheets and endless rows of numbers.
- Enhanced Engagement: Stakeholders are more likely to engage with and trust the insights provided when data is presented visually, as it supports more intuitive and memorable information processing.
- Data Storytelling: Well-designed visualizations can effectively tell a narrative, providing context and meaning that lead to better business decisions.
Investing in intuitive analytics tools that provide robust visualization options can significantly enhance the ability to communicate insights effectively across the organization.
